Are you ready to elevate your photography skills to a professional level? Capturing stunning images with a digital camera is more than just pointing and shooting. To truly excel in the world of photography, you need to understand the technical aspects of your camera, as well as develop an artistic eye for composition and lighting.
In this guide, we will explore the essential tips and techniques that will help you take pictures like a pro using your digital camera. Whether you’re a beginner looking to learn the basics or an experienced photographer aiming to enhance your craft, this comprehensive resource will provide you with the knowledge and inspiration you need to create captivating images.
Mastering the Basics
Before diving into advanced photography techniques, it’s essential to master the basics of using your digital camera. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Understanding Your Camera Settings
- Take the time to familiarize yourself with the various settings on your camera, such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO.
- Experiment with different settings to understand how they affect the outcome of your photos.
Practicing Proper Composition
- Learn about the rule of thirds and other composition techniques to create visually appealing photos.
- Pay attention to framing, leading lines, and the background to compose your shots effectively.
By mastering these basics, you’ll be better equipped to take stunning photos with your digital camera like a pro.
Understanding Camera Settings
One of the key factors in taking professional-quality photos with a digital camera is understanding how to adjust the camera settings. Here are some important settings you should be familiar with:
1. Aperture: The aperture setting controls the amount of light that enters the camera. A lower aperture number (e.g. f/2.8) allows more light in, while a higher aperture number (e.g. f/16) lets in less light. Adjusting the aperture also affects the depth of field in your photos.
2. Shutter Speed: Shutter speed determines how long the camera’s shutter remains open when taking a photo. A faster shutter speed (e.g. 1/1000s) freezes motion, while a slower shutter speed (e.g. 1/30s) creates a sense of motion blur. Experiment with different shutter speeds to capture the desired effect.
3. ISO: ISO measures the camera sensor’s sensitivity to light. A lower ISO (e.g. 100) is ideal for bright conditions, while a higher ISO (e.g. 1600) is suitable for low-light situations. Be cautious, as higher ISO settings can introduce noise into your photos.
4. White Balance: White balance adjusts the color temperature of your photos to ensure accurate color reproduction. Different lighting conditions require different white balance settings, such as daylight, cloudy, or tungsten. Experiment with white balance presets or manually adjust the setting to achieve the desired color balance.
By mastering these camera settings and understanding how they interact with each other, you can elevate your photography skills and take stunning photos like a pro.
Choosing the Right Lens
When it comes to taking professional-quality photos with your digital camera, choosing the right lens is crucial. The lens you use can greatly impact the quality and style of your photos. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a lens:
Focal Length
The focal length of a lens determines how much of the scene will be captured in your photo. A shorter focal length, such as a wide-angle lens, is great for capturing landscapes and large group shots. On the other hand, a longer focal length, like a telephoto lens, is ideal for getting close-up shots of distant subjects.
Aperture
The aperture of a lens controls the amount of light that enters the camera. A wider aperture (lower f-stop number) allows more light to reach the sensor, making it ideal for low-light situations and achieving a shallow depth of field. On the other hand, a narrower aperture (higher f-stop number) is better for capturing sharp images with a greater depth of field.
| Lens Type | Best For |
| Wide-angle | Landscapes, architecture, group shots |
| Telephoto | Wildlife, sports, portraits |
| Prime | Low-light conditions, portrait photography |
| Zoom | Versatility, travel photography |
Consider these factors when choosing the right lens for your digital camera to ensure that you capture stunning photos like a pro.
Composition Techniques
Composition is key to capturing stunning photographs with your digital camera. Here are some composition techniques to help you take your photos to the next level:
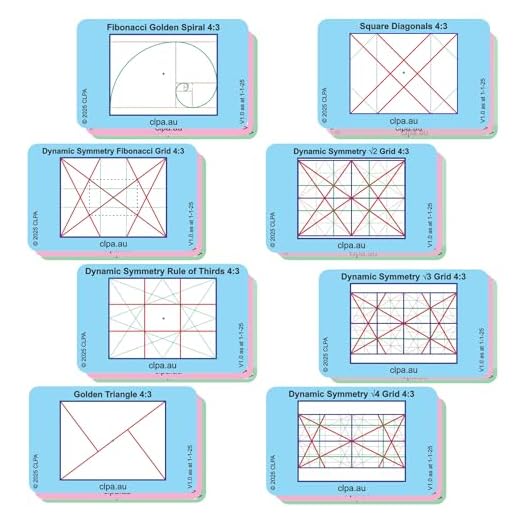
Rule of Thirds
The rule of thirds is a basic composition technique where you divide your frame into a 3×3 grid and place your subject along the gridlines or at the intersections. This creates a more visually appealing and balanced composition.
Leading Lines
Leading lines are lines within the frame that lead the viewer’s eye towards the main subject of the photo. Look for natural lines such as roads, fences, or rivers to guide the viewer’s gaze and create a sense of depth in your photos.
Rule of Thirds
The rule of thirds is a fundamental principle in photography that can help you compose visually appealing and balanced images. The idea is to divide your frame into a grid of nine equal sections by drawing two horizontal and two vertical lines. The key elements of your composition, such as the main subject or points of interest, should be placed along these lines or their intersections. This technique creates a sense of balance and harmony in your photos, making them more engaging to the viewer’s eye.
Leading Lines
Leading lines are a powerful compositional tool in photography that can help guide the viewer’s eye through the image. They are lines within the image that lead the viewer’s gaze towards the main subject or focal point of the photograph. These lines can be anything from roads, fences, buildings, or even natural elements like rivers or tree branches. By using leading lines effectively, you can create a sense of depth and perspective in your photos.
When composing your shot, look for lines that can lead the viewer’s eye towards your subject. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to see how the lines interact with the rest of the elements in your image. Remember that leading lines don’t always have to be straight – curved or diagonal lines can also create dynamic compositions.
Pro tip: Pay attention to the placement of the leading lines in your frame. Try to position them in a way that enhances the overall composition and draws the viewer’s attention to the main subject. Don’t be afraid to experiment and play around with different compositions to see what works best for your image.
Lighting Tips
2. Avoid harsh overhead lighting. Direct sunlight can create harsh shadows and overexposure. Look for shaded areas or use a diffuser to soften the light.
3. Experiment with different lighting angles. Try shooting from different angles to see how the light interacts with your subject. Side lighting can create depth and texture, while backlighting can add drama to your photos.
4. Consider using artificial lighting. If natural light is not available or insufficient, consider using artificial lighting sources such as flash or studio lights. Experiment with different lighting setups to achieve the desired effect.
5. Use reflectors to bounce light. Reflectors can help to fill in shadows and create a more even lighting across your subject. Silver reflectors provide a cooler light, while gold reflectors add warmth to your photos.
6. Pay attention to white balance. Adjust the white balance settings on your camera to ensure accurate color reproduction under different lighting conditions. This will help you achieve more natural-looking photos.
Natural vs Artificial Light
Lighting is a key element in photography, and understanding the difference between natural and artificial light can help you capture stunning images.
Natural Light
Natural light is light that comes from the sun. It is often considered the most flattering type of light for photography because it is soft and diffused. The best times to shoot in natural light are during the golden hours, which occur shortly after sunrise and before sunset. This type of light creates warm, soft shadows and is ideal for capturing portraits and landscapes.
Artificial Light
Artificial light is light produced by man-made sources such as lamps, flashlights, and studio lights. While artificial light can be manipulated and controlled more easily than natural light, it can also create harsh shadows and unnatural colors. When using artificial light, it’s important to experiment with different angles and intensities to achieve the desired effect.
Using Reflectors
Reflectors are essential tools for professional photographers to manipulate light and create stunning images. They come in various sizes and colors, such as silver, gold, white, and black, each serving a different purpose.
When using a reflector, position it strategically to bounce light onto your subject. For example, a silver reflector can add a cool, metallic sheen to your photos, while a gold reflector can create warm, flattering light. A white reflector is great for softening harsh shadows, and a black reflector can add drama and depth to your images.
Experiment with different angles and distances to see how the reflector affects the light and shadows in your photos. With practice, you’ll learn how to use reflectors effectively to enhance your photography and take your images to the next level.